- Published Jan 24, 2014 in Music 101
Vinyl records don't just end up sounding good on their own. That's what standards and practices are for.
The Recording Industry Association of America developed a standard playback equalization curve and required that all LP records and record players manufactured conform to this standard.
You have probably noticed that you cannot take the audio plugs from your turntable and plug them into an ordinary line input connection on your preamp. (Well, you can, but it sounds horrible.) The line input connections, designed for tape machines and CD players, do not have the RIAA curve. Every phono pre-amp must have this playback equalization built into it. Since most of you are probably not audio engineers, I’ll try to describe this curve by explaining why it was used.
The only way the LP works to make pleasing realistic music is for the audio to be pre-EQ’d…
If you were to cut an ordinary audio source (without the RIAA EQ) into a lacquer at a reasonably hot level you would notice two things: First, the bass frequencies, with their long wavelengths, are so big and loud that they cause the groove to make really large squiggles. So large, in fact, that it would be hard for a cartridge to playback the squiggles. These very large cut grooves would take up a huge amount of space on the disk and limit your playing time to only a few minutes on a 12″ LP side.
The second thing you would notice is that records are noisy. Yeah I know, you already know that. But I mean a vinyl record is REALLY noisy. That audio source played back without the EQ would be mostly scratchy noise and clicks like you’ve heard from an Edison Cylinder. The only way the LP works to make pleasing realistic music is for the audio to be pre-EQ’d so that the bass is reduced dramatically—by 20dB—and the treble is increased dramatically, also by 20dB. The original music returns when the opposite EQ is applied by the phono preamp.
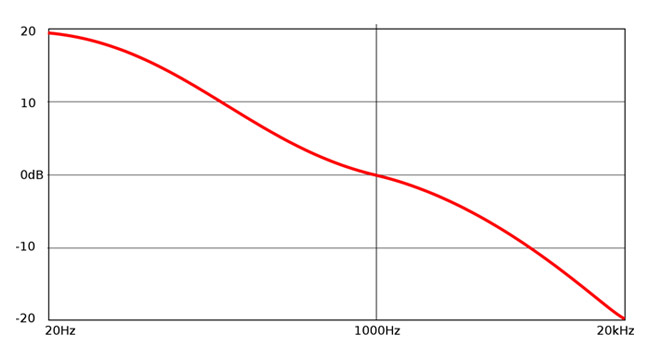
The RIAA curve, developed by the Recording Industry Association of America.
See the picture above—this is the playback curve when the bass is boosted back up 20dB and the high frequencies are rolled off. The reduction in bass helps us get the twenty plus minutes per side, and the exaggerated treble works as a very effective noise reduction. You see, the audio had it’s treble boosted before it was cut. Then surface noise from the vinyl was introduced on playback. When played back through the complementary filter, the high end is cut and the surface noise is reduced, but the audio returns to it’s original frequency response. Like magic. The resulting bass response of the LP was better than a 78 too – by a lot. And the noise floor was improved.
So that’s why an equalization curve was developed, and why the RIAA standardized it.
But even that’s not the end of the story. The big treble boost puts extreme stress on the cutting amplifiers; so much so that specially built circuit breakers need to be inline at all times to avoid damaging the (very expensive) cutter head. This high frequency emphasis also causes bright instruments like cymbals and vocals to distort if cut without care.
Listen to this quick before and after. It’s a sample of a track by the artist Danni (produced by Nik Fairclough).
First, here’s the track without the RIAA curve applied:
You will immediately notice the almost painfully shrill top end and dramatic loss of bass from the RIAA filter. It was never intended that the end user ever hear the RIAA encoded signal — a good thing, because it sounds terrible.
This example illustrates just how much the music has to be pre-emphasized to effectively reduce the surface noise of the disk:
That’s it for my crash course on the vinyl groove and the RIAA curve. On to more aspects of vinyl next week!

